Polygraph vs. Lie Detector: What’s the Difference
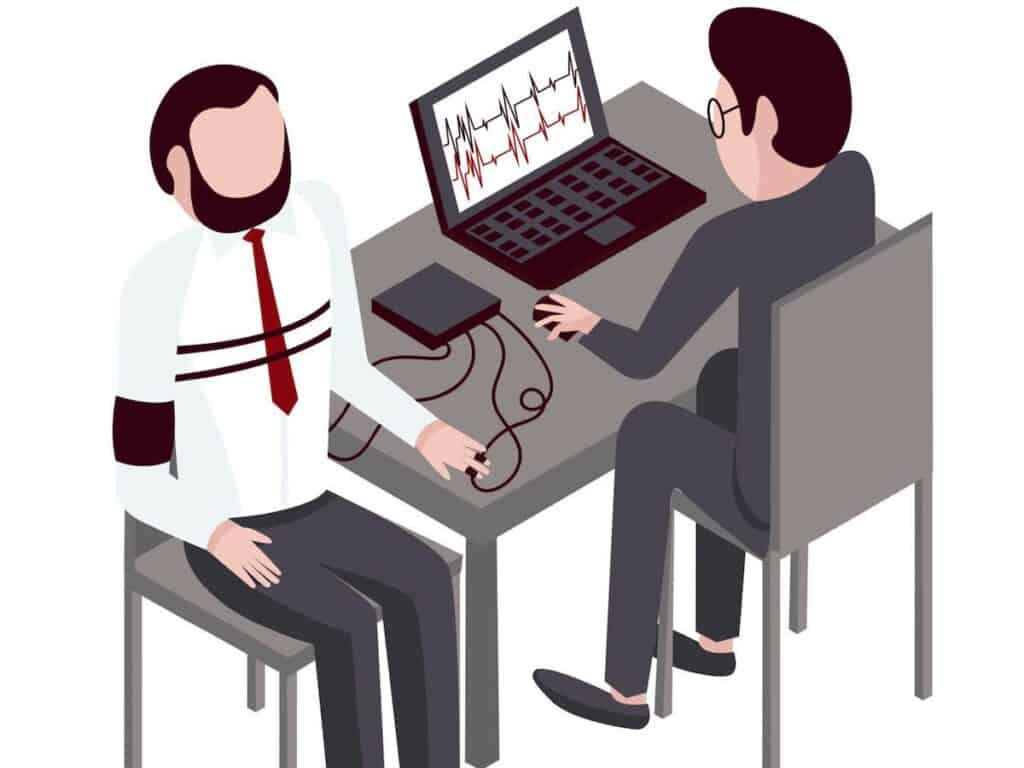
A polygraph test is more commonly referred to as a lie detector test. The former sounds more scientific, while the latter sounds more layman. But are polygraphs and lie detectors really one and the same when police officers, detectives, lawyers and employers talk about them?
Yes, polygraphs are lie detectors and lie detectors are polygraphs. However, the term lie detector is a misnomer because a polygraph detects bodily changes that can be linked to lying rather than lying itself. No matter if in law enforcement, court trials or for employment applications, lie detection is a broad term, which includes polygraphy.
About to be asked yes or no questions while strapped to a machine? Read on.
In this post, we will talk about the things that separate a polygraph from a lie detector. You will learn that even though they are used interchangeably, there are subtle differences between them.
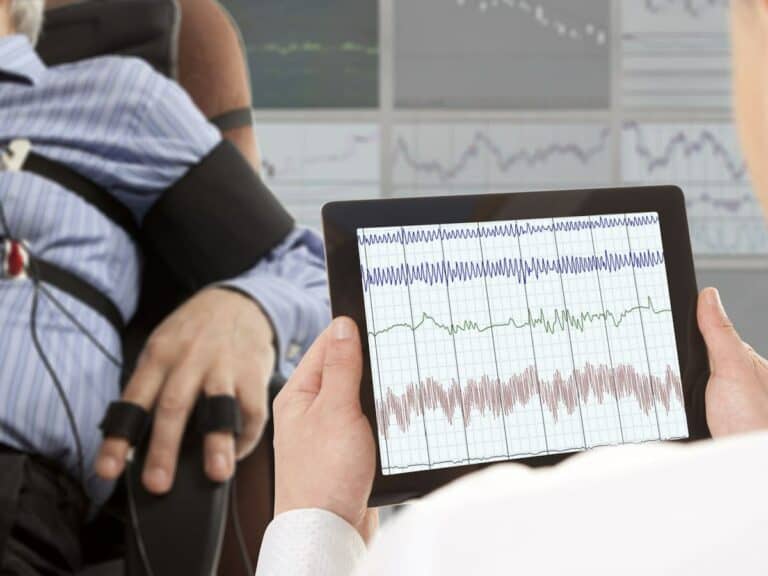
The Polygraph Examination
Back in 1878, Angelo Mosso, who was an Italian physiologist, measured a handful of physiological reactions of individuals when being questioned: cardiovascular and respiratory responses. The equipment he used to carry out the task was referred to as a plethysmograph.

He grabbed the attention of various scientists, prompting them to improve on his studies.
The initial version of the polygraph machine was invented in 1921 by John Larson, who was a Canadian psychologist, while he was working for the Berkeley Police Department in Berkeley, California. He named his invention after the Greek word “polygraphos”, which translates to “much writing” in English.
During that time, the instrument was only capable of reading blood pressure, heart rate and respiratory rate. In 1938, however, Leonarde Keeler, who is recognized as the co-inventor of the polygraph, integrated a couple of sensors into the machine. The additional sensors allowed for the measurement of the galvanic skin response or sweating.
Polygraph machines these days are digital or computerized — analog ones are commonly used by police officers and criminal investigators as backup devices.
It’s also on forensics crime drama TV shows and movies where you can see analog polygraph instruments.
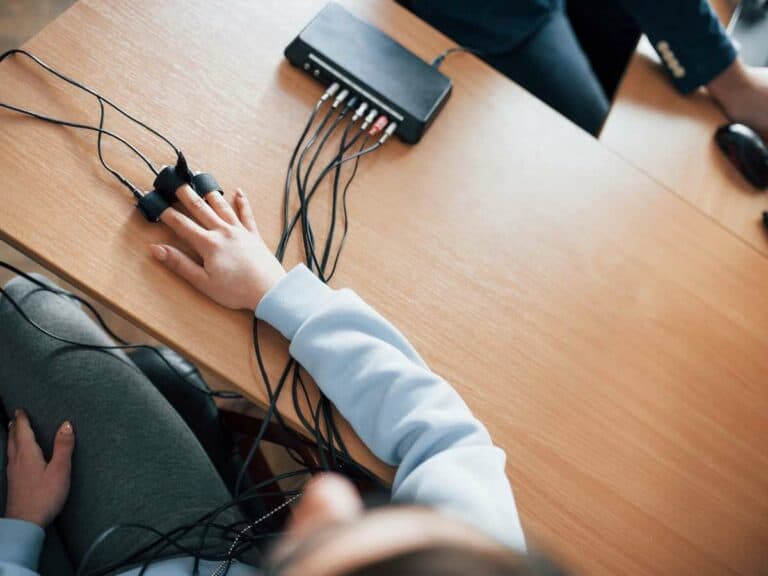
Although a polygraph test is also oftentimes referred to as a lie detector test, it’s not really the most accurate moniker for it. That’s because a polygraph machine is not really engineered to detect a lie.
What it does is monitor the level of stress, fear and anxiety as the subject answers questions.
One of the most important things a polygraph examiner has to carry out is to tell apart the differences in the physiological processes of the examinee when being truthful and for when being deceitful. Such is done by asking irrelevant questions and control questions before asking relevant questions or questions related to the crime being investigated.
Irrelevant questions do not elicit a strong response from the individual because they are easy to answer and require no lying. The readings obtained serve as the baseline for truthfulness.
On the other hand, control questions can cause a surge of stress or panic in the examinee for they are difficult to answer and, in most instances, prompt the person to lie. The readings obtained by the polygraph machine serve as the baseline for deception. Analyzing the readings throughout the test allows the examiner to come up with a verdict.
Whenever the examinee answers a relevant question truthfully, the readings will be closer to the baseline for truthfulness. Meanwhile, they will be closer to the baseline readings for deception when he or she answers dishonestly.
Other Lie Detector Tests
Some individuals choose to refer to it as a polygraph test. Others, meanwhile, prefer to call it a lie detector test. But, as mentioned earlier, a lie detector test can also be anything else than a polygraph test.
In this part of this post, I will briefly talk about a couple of other lie detector examination types.
They are less popular than a polygraph test, which means that it’s less likely that you will undergo any of them in this lifetime. Still, since they are around and being conducted, it’s a good idea to be acquainted with them if you’re interested in all sorts of truth-telling methods used in criminal investigations.
Narco Analysis
During a polygraph test, the examinee can be either truthful or deceitful. It’s an entirely different thing when the subject is undergoing what’s referred to as narco analysis — he or she can only be truthful.
That’s because truth serum is injected into the body of the person.
Whether sodium pentothal or sodium amytal is the truth serum of choice, the same effect is achieved: after its administration, the examinee slips into a semi-conscious state. While in this state, the individual being questioned would have not the ability to cook up a lie.
So, in other words, the person’s answer to each and every question asked would only be restricted to facts that he or she is already aware of, thus causing nothing to come out of his or her mouth but the truth.
The problem with narco analysis is that it’s quite risky and dangerous.
Injecting an amount of truth serum inappropriate for the examinee’s age and physical condition, for instance, can result in a coma or even death. It’s exactly due to this why a team of professionals, which includes a physician and a nurse, is around during narco analysis instead of just a trained and experienced polygraph examiner.
Narco analysis is practically just as old as the polygraph, which came into being in 1921 — it was first used in the criminal investigation of 2 prisoners in the US back in 1922.
Brain Mapping
A polygraph test measures and records an assortment of physiological processes in the subject of the examination. They include the blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory activity and sweating.
On the other hand, brain mapping focuses on only a single thing: brain wave patterns.
Just like the vitals, brain wave patterns are different for when the individual is telling the truth and for when he or she is stating a lie. The said changes can be monitored with the help of small metal discs called electrodes placed on various areas of the examinee’s head. Essentially, brain mapping is similar to EEG.
Short for electroencephalogram, EEG is a diagnostic method commonly used for evaluating all kinds of brain disorders, including epilepsy and other seizure disorders.
The process of brain mapping requires the subject of the lie detector test to wear a cap, onto which a total of 20 electrodes are attached. The entire process can take anywhere from 15 minutes to 2 hours to complete, depending on the examination’s administrator, the nature of the test and the number of questions asked.
According to a report by Penn Today, which is the daily online publication of the University of Pennsylvania, brain mapping is more accurate than a polygraph examination. As a matter of fact, the said report adds that, based on research, brain mapping is 24% more likely to detect lies than a polygraph.
Brain mapping is a lot younger than a polygraph test — it was invented in the 1970s when both magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scan techniques were being created.
Read Also: Polygraph: 11 Advantages and 11 Disadvantages
Just Before You Go and Undergo the Test
While the term lie detector test is a misnomer, it’s generally accepted as another term for a polygraph test. But technically speaking, a polygraph test is just one example of a lie detector test, which also comes in other forms.
Related Questions
Can you choose a polygraph examiner?
When seeking a lie detector test for cheating or infidelity, the couple can choose which examiner or testing center to use. For investigative or pre-employment screening purposes, however, it’s the one who requires the lie detector examination who chooses which polygraph expert will conduct the test.
Check Also: Where You Can Get a Polygraph Test In Your State
What happens if you are nervous during a polygraph test?
A polygraph machine cannot detect lies. Rather, it’s designed to observe physiological processes such as blood pressure and respiratory rate. Since a lie detector test cannot differentiate the readings between nervousness and deception, the task is left in the hands of the examiner.